Lyubov L Kuchkarova
National University of Uzbekistan, Uzbekistan
Title: Correcting effect of some biological substance on digestive disorders at heavy metal intoxication
Biography
Biography: Lyubov L Kuchkarova
Abstract
Statement of the Problem: It is known that increasing of heavy metal pollution is correlated with increasing of gastrointestinal diseases. This suggests the need to find ways to mass prevention and/or correction of digestive disorders at heavy metal intoxication, especially in industrial regions. The purpose of current study is testing some of the biological substrates to correct heavy metal caused digestive disorders.
Methods: Morphological and functional characteristics of the gastrointestinal tract have been obtained during multiple experiments with administration of biologically active substances to intoxicated with heavy metal laboratory animals.
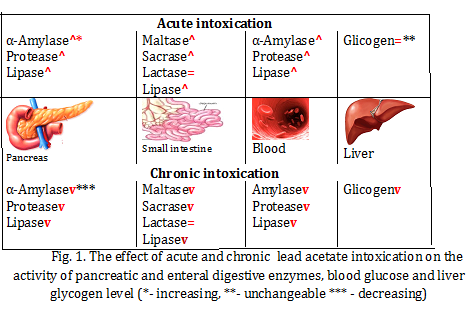
Findings: Ðcute toxicity of cadmium, lead and/or mercury ions results in adaptive shifts in the pancreatic and intestinal enzyme activity to preserve energy homeostasis. Chronic intoxication with heavy metals leads to the development of pancreatitis, diabetes, malabsorption and other digestive disorders. For the prevention and/or correction of heavy metal intoxication among the tested biological substrates (flavonoids, terpenoids and non-starch polysaccharides) the most effective were non-starch polysaccharides (chitosan, inulin and pectin).
Conclusion: These data suggest that adding non-starch polysaccharides in the diet may promotes the correction of pathological changes in the gastrointestinal tract in heavy metal-contaminated areas.